一、Executor框架簡介
1、基礎簡介
Executor系統中,將線程任務提交和任務執行進行了解耦的設計,Executor有各種功能強大的實現類,提供便捷方式來提交任務並且獲取任務執行結果,封裝了任務執行的過程,不再需要Thread().start()方式,顯式創建線程並關聯執行任務。
2、調度模型
線程被一對一映射為服務所在操作系統線程,啟動時會創建一個操作系統線程;當該線程終止時,這個操作系統線程也會被回收。
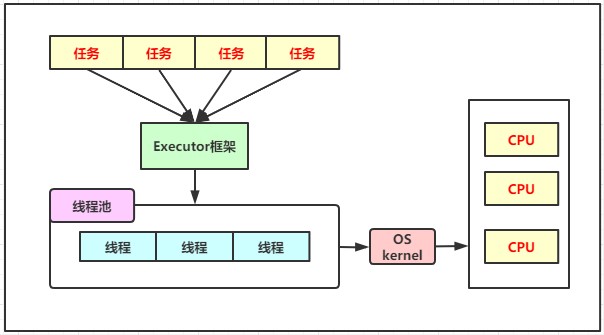
3、核心API結構
Executor框架包含的核心接口和主要的實現類如下圖所示:
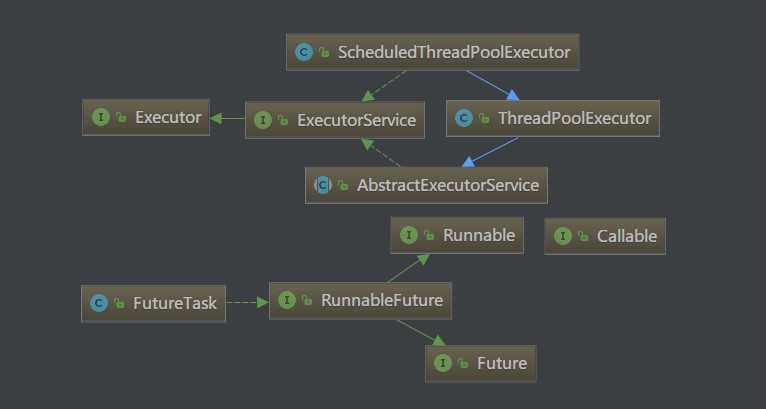
線程池任務:核心接口:Runnable、Callable接口和接口實現類;
任務的結果:接口Future和實現類FutureTask;
任務的執行:核心接口Executor和ExecutorService接口。在Executor框架中有兩個核心類實現了ExecutorService接口,ThreadPoolExecutor和ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
二、用法案例
1、API基礎
ThreadPoolExecutor基礎構造
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {}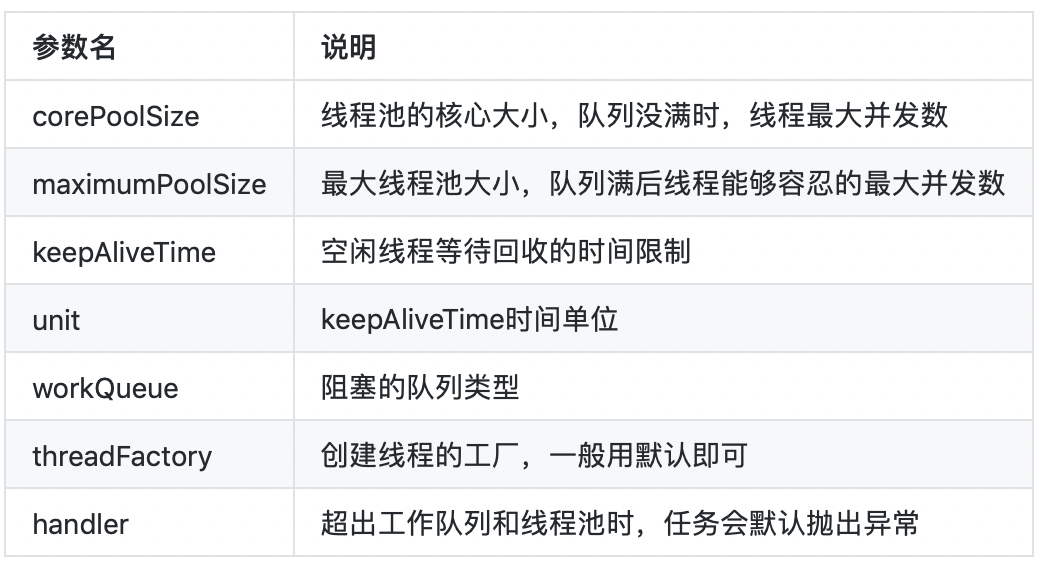
2、初始化方法
ExecutorService :Executors.newFixedThreadPool();
ExecutorService :Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ExecutorService :Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ThreadPoolExecutor :new ThreadPoolExecutor() ;通常情況下,線程池不允許使用Executors去創建,而是通過ThreadPoolExecutor的方式,這樣的處理方式更加明確線程池的運行規則,規避資源耗盡的風險。
3、基礎案例
package com.multy.thread.block08executor;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Executor01 {
// 定義線程池
private static ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
3,10,5000,TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<>(),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),new ExeHandler());
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++){
poolExecutor.execute(new PoolTask(i));
//帶返回值:poolExecutor.submit(new PoolTask(i));
}
}
}
// 定義線程池任務
class PoolTask implements Runnable {
private int numParam;
public PoolTask (int numParam) {
this.numParam = numParam;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("PoolTask "+ numParam+" begin...");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public int getNumParam() {
return numParam;
}
public void setNumParam(int numParam) {
this.numParam = numParam;
}
}
// 定義異常處理
class ExeHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable runnable, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.out.println("ExeHandler "+executor.getCorePoolSize());
executor.shutdown();
}
}流程分析
- 線程池中線程數小於corePoolSize時,新任務將創建一個新線程執行任務,不論此時線程池中存在空閒線程;
- 線程池中線程數達到corePoolSize時,新任務將被放入workQueue中,等待線程池中任務調度執行;
- 當workQueue已滿,且maximumPoolSize>corePoolSize時,新任務會創建新線程執行任務;
- 當workQueue已滿,且提交任務數超過maximumPoolSize,任務由RejectedExecutionHandler處理;
- 當線程池中線程數超過corePoolSize,且超過這部分的空閒時間達到keepAliveTime時,回收該線程;
- 如果設置allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true)時,線程池中corePoolSize範圍內的線程空閒時間達到keepAliveTime也將回收;
三、線程池應用
應用場景:批量賬戶和密碼的校驗任務,在實際的業務中算比較常見的,通過初始化線程池,把任務提交執行,最後拿到處理結果,這就是線程池使用的核心思想:節省資源提升效率。
public class Executor02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化校驗任務
List<CheckTask> checkTaskList = new ArrayList<>() ;
initList(checkTaskList);
// 定義線程池
ExecutorService executorService ;
if (checkTaskList.size() < 10){
executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(checkTaskList.size());
}else{
executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
}
// 批量處理
List<Future<Boolean>> results = new ArrayList<>() ;
try {
results = executorService.invokeAll(checkTaskList);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
// 查看結果
for (Future<Boolean> result : results){
try {
System.out.println(result.get());
// System.out.println(result.get(10000,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace() ;
}
}
// 關閉線程池
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
private static void initList (List<CheckTask> checkTaskList){
checkTaskList.add(new CheckTask("root","123")) ;
checkTaskList.add(new CheckTask("root1","1234")) ;
checkTaskList.add(new CheckTask("root2","1235")) ;
}
}
// 校驗任務
class CheckTask implements Callable<Boolean> {
private String userName ;
private String passWord ;
public CheckTask(String userName, String passWord) {
this.userName = userName;
this.passWord = passWord;
}
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
// 校驗賬戶+密碼
if (userName.equals("root") && passWord.equals("123")){
return Boolean.TRUE ;
}
return Boolean.FALSE ;
}
}線程池主要用來解決線程生命週期開銷問題和資源不足問題,通過線程池對多個任務線程重複使用,線程創建也被分攤到多個任務上,多數任務提交就有空閒的線程可以使用,所以消除線程頻繁創建帶來的開銷。
四、源代碼地址
GitHub·地址
https://github.com/cicadasmile/java-base-parent
GitEE·地址
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/java-base-parent