hashMap 應該是java程序員工作中用的比較多的一個鍵值對處理的數據的類型了。這種數據類型一般都會有增刪查的方法,今天我們就來看看它的循環方法以前寫過一篇關於ArrayList的循環效率問題《ArrayList哪種遍歷效率最好,你真的弄明白了嗎?》,感興趣的同學可以去看看。hashMap 有常見的六七種遍歷的方式。這麼多的選擇,大家平時都是使用哪一種來遍歷數據列?歡迎大家在下方留言哦。說實話這麼多種方式,想記也不記不住,也不想浪費時間來記這玩意,所以本人在JDK1.8以前基本上都是用Map.Entry的方式來遍歷,1.8及以後就習慣性用forEach了,不過這個不能有continue或者break操作這個有時候還是挺不方便的,其他幾種基本上沒怎麼用過,也沒太研究這幾種方式,哪種性能是比較好的。反正就是挑自己熟悉的方式。好了話不多說,我們還是直入今天的主題。先來看看每種遍歷的方式:
在for循環中使用entries實現Map的遍歷
public static void forEachEntries() {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
String mapKey = entry.getKey();
String mapValue = entry.getValue();
}
}
在for循環中遍歷key
public static void forEachKey() {
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
String mapKey = key;
String mapValue = map.get(mapKey);
}
}
在for循環中遍歷value
public static void forEachValues() {
for (String key : map.values()) {
String val = key;
}
}
Iterator遍歷
public static void forEachIterator() {
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (entries.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, String> entry = entries.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
}
}
forEach jdk1.8遍歷
public static void forEach() {
map.forEach((key, val) -> {
String key1 = key;
String value = val;
});
}
Stream jdk1.8遍歷
map.entrySet().stream().forEach((entry) -> {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
});
Streamparallel jdk1.8遍歷
public static void forEachStreamparallel() {
map.entrySet().parallelStream().forEach((entry) -> {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
});
}
以上就是常見的對於map的一些遍歷的方式,下面我們來寫個測試用例來看下這些遍歷方式,哪些是效率最好的。下面測試用例是基於JMH來測試的
首先引入pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId>
<artifactId>jmh-core</artifactId>
<version>1.23</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId>
<artifactId>jmh-generator-annprocess</artifactId>
<version>1.23</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
關於jmh測試如可能會影響結果的一些因素這裡就不詳細介紹了,可以參考文末的第一個鏈接寫的非常詳細。以及測試用例為什麼要這麼寫(都是為了消除JIT對測試代碼的影響)這是參照官網的鏈接:
編寫測試代碼如下:
package com.workit.autoconfigure.autoconfigure.controller;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.*;
import org.openjdk.jmh.infra.Blackhole;
import org.openjdk.jmh.results.format.ResultFormatType;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.Runner;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.RunnerException;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.Options;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.OptionsBuilder;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
- @author:公眾號: java金融
- @Date:
- @Description:微信搜一搜【java金融】回覆666
*/
@State(Scope.Thread)
@Warmup(iterations = 5, time = 1, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
@Measurement(iterations = 5, time = 1, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
@Fork(1)
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)
public class InstructionsBenchmark {
public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {
Options opt = new OptionsBuilder().include(InstructionsBenchmark.class.getSimpleName()).result("result.json").resultFormat(ResultFormatType.JSON).build();
new Runner(opt).run();
}
static final int BASE = 42;
static int add(int key,int val) {
return BASE + key +val;
}
@Param({"1", "10", "100", "1000","10000","100000"})
int size;
private static Map<Integer, Integer> map;
// 初始化方法,在全部Benchmark運行之前進行
@Setup(Level.Trial)
public void init() {
map = new HashMap<>(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
map.put(i, i);
}
}
/**
* 在for循環中使用entries實現Map的遍歷:
*/
@Benchmark
public static void forEachEntries(Blackhole blackhole) {
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer mapKey = entry.getKey();
Integer mapValue = entry.getValue();
blackhole.consume(add(mapKey,mapValue));
}
}
/**
* 在for循環中遍歷key
*/
@Benchmark
public static StringBuffer forEachKey(Blackhole blackhole) {
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
// Integer mapValue = map.get(key);
blackhole.consume(add(key,key));
}
return stringBuffer;
}
/**
* 在for循環中遍歷value
*/
@Benchmark
public static void forEachValues(Blackhole blackhole) {
for (Integer key : map.values()) {
blackhole.consume(add(key,key));
}
}
/**
* Iterator遍歷;
*/
@Benchmark
public static void forEachIterator(Blackhole blackhole) {
Iterator<Entry<Integer, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (entries.hasNext()) {
Entry<Integer, Integer> entry = entries.next();
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
blackhole.consume(add(key,value));
}
}
/**
* forEach jdk1.8遍歷
*/
@Benchmark
public static void forEachLamada(Blackhole blackhole) {
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
blackhole.consume(add(key,value));
});
}
/**
* forEach jdk1.8遍歷
*/
@Benchmark
public static void forEachStream(Blackhole blackhole) {
map.entrySet().stream().forEach((entry) -> {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
blackhole.consume(add(key,value));
});
}
@Benchmark
public static void forEachStreamparallel(Blackhole blackhole) {
map.entrySet().parallelStream().forEach((entry) -> {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
blackhole.consume(add(key,value));
});
}
}
運行結果如下:
注:運行環境idea 2019.3,jdk1.8,windows7 64位。
Benchmark (size) Mode Cnt Score Error Units
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachEntries 1 avgt 5 10.021 ± 0.224 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachEntries 10 avgt 5 71.709 ± 2.537 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachEntries 100 avgt 5 738.873 ± 12.132 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachEntries 1000 avgt 5 7804.431 ± 136.635 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachEntries 10000 avgt 5 88540.345 ± 14915.682 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachEntries 100000 avgt 5 1083347.001 ± 136865.960 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachIterator 1 avgt 5 10.675 ± 2.532 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachIterator 10 avgt 5 73.934 ± 4.517 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachIterator 100 avgt 5 775.847 ± 198.806 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachIterator 1000 avgt 5 8905.041 ± 1294.618 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachIterator 10000 avgt 5 98686.478 ± 10944.570 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachIterator 100000 avgt 5 1045309.216 ± 36957.608 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachKey 1 avgt 5 18.478 ± 1.344 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachKey 10 avgt 5 76.398 ± 12.179 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachKey 100 avgt 5 768.507 ± 23.892 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachKey 1000 avgt 5 11117.896 ± 1665.021 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachKey 10000 avgt 5 84871.880 ± 12056.592 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachKey 100000 avgt 5 1114948.566 ± 65582.709 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachLamada 1 avgt 5 9.444 ± 0.607 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachLamada 10 avgt 5 76.125 ± 5.640 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachLamada 100 avgt 5 861.601 ± 98.045 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachLamada 1000 avgt 5 7769.714 ± 1663.914 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachLamada 10000 avgt 5 73250.238 ± 6032.161 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachLamada 100000 avgt 5 836781.987 ± 72125.745 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStream 1 avgt 5 29.113 ± 3.275 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStream 10 avgt 5 117.951 ± 13.755 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStream 100 avgt 5 1064.767 ± 66.869 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStream 1000 avgt 5 9969.549 ± 342.483 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStream 10000 avgt 5 93154.061 ± 7638.122 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStream 100000 avgt 5 1113961.590 ± 218662.668 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStreamparallel 1 avgt 5 65.466 ± 5.519 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStreamparallel 10 avgt 5 2298.999 ± 721.455 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStreamparallel 100 avgt 5 8270.759 ± 1801.082 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStreamparallel 1000 avgt 5 16049.564 ± 1972.856 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStreamparallel 10000 avgt 5 69230.849 ± 12169.260 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachStreamparallel 100000 avgt 5 638129.559 ± 14885.962 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachValues 1 avgt 5 9.743 ± 2.770 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachValues 10 avgt 5 70.761 ± 16.574 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachValues 100 avgt 5 745.069 ± 329.548 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachValues 1000 avgt 5 7772.584 ± 1702.295 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachValues 10000 avgt 5 74063.468 ± 23752.678 ns/op
InstructionsBenchmark.forEachValues 100000 avgt 5 994057.370 ± 279310.867 ns/op
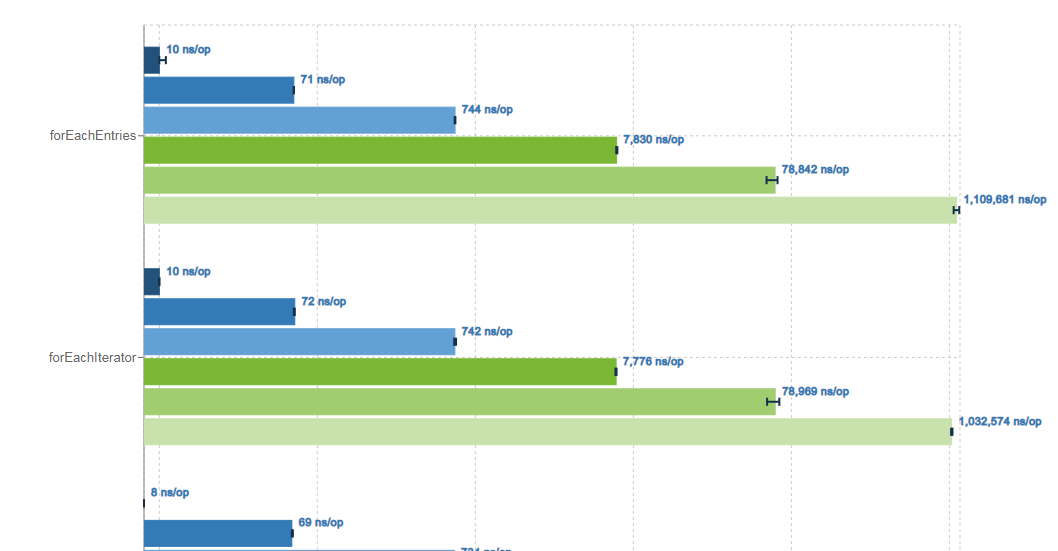
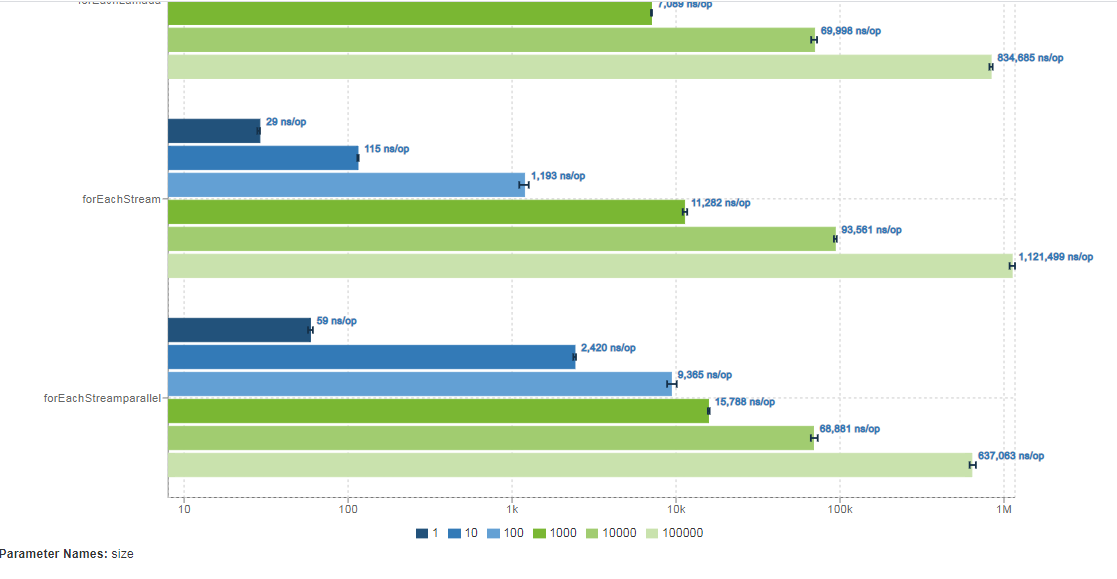
通過上述的圖我們可以發現,數據量較小的時候forEachEntries和forEachIterator、以及lamada循環效率都差不多forEachStreamarallel的效率反而較低,只有當數據量達到10000以上parallelStream的優勢就體現出來了。所以平時選擇使用哪種循環方式的時候沒必要太糾結哪一種方式,其實每種方式之間的效率還是微乎其微的。選擇適合自己的就好。為什麼parallelStream在數據量較小的時候效率反而不行?這個大家可以在下方留言哦。
總結
上面小實驗只是在我機器上跑出來的結果,可能放到不同的機器運行結果有不一樣哦,大家感興趣的同學可以把代碼貼到自己的機器上跑一跑,也許我這這個結論就不適用了。
結束
- 由於自己才疏學淺,難免會有紕漏,假如你發現了錯誤的地方,還望留言給我指出來,我會對其加以修正。
- 如果你覺得文章還不錯,你的轉發、分享、讚賞、點贊、留言就是對我最大的鼓勵。
- 感謝您的閱讀,十分歡迎並感謝您的關注。
巨人的肩膀摘蘋果:
https://www.cnkirito.moe/java-jmh/
https://jmh.morethan.io/