本文通過展示主機監控, 數據庫監控, 應用監控幫助用戶完成從基礎設施到業務層面的監控, 我們在每個示例中使用不同的數據採集和可視化實現方式, 幫助用戶全面瞭解SLS提供的時序監控能力
監控層次
在我們實施監控時, 服務端監控至少包含以下部分:

基礎設施&網絡在雲時代絕大多數用戶已經不再需要關心, 因此我們主要關心操作系統/數據庫&中間件以及應用&業務的監控
SLS擁抱開源, 可以藉助成熟的監控軟件提供的能力, 如Prometheus, telegraf, Grafana等, 構建靈活的解決方案.
靈活的數據收集方案
例如Prometheus支持眾多Exporter, 並且是kubernetes標配, 那麼我們可以選擇用Prometheus exporter暴露數據, 用Prometheus進行採集, 通過remote write協議寫入Metric Store(參見文檔: 採集Prometheus監控數據_數據接入_時序存儲_日誌服務-阿里雲), 下文將以Java應用監控為例展示該用法
telegraf同樣支持眾多采集插件, 因此也可以選擇用telegraf進行採集, 並通過influxdb的協議寫入Metric Store, 下文將以MySQL監控為例展示該用法
同時SLS的logtail本身也有采集能力, 因此也可以使用logtail進行採集, 例如我們提供的主機監控: 採集主機監控數據_數據接入_時序存儲_日誌服務-阿里雲
查詢基礎
在展示具體例子之前, 我們先學習一點查詢語法作為基礎
SLS Metric Store支持使用SQL + PromQL進行查詢, 使用方法為使用PromQL函數進行查詢, 然後可將該查詢作為子查詢嵌套完整SQL語法:
SELECT
promql_query_range('up', '1m')
FROM metrics;
SELECT
sum(value)
FROM
(SELECT promql_query_range('up', '1m')
FROM metrics);其中promql_query_range的第一個參數就是PromQL, 第二個參數為step, 即時間粒度 在MetricStore查詢頁面中, 可在Metrics下拉框中選擇指標, 會自動生成最簡單的查詢, 點擊預覽即可看到圖表: 
PromQL語法入門
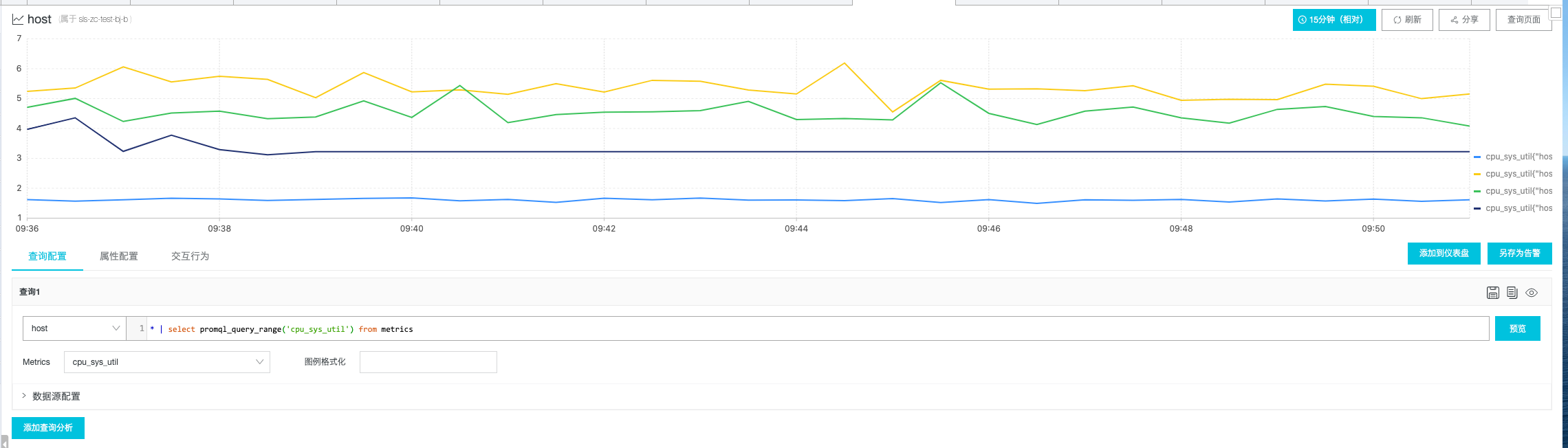
例子:
avg(go_gc_duration_seconds{endpoint = “http-metrics”}) by (instance)完整PromQL語法可查看Prometheus官方文檔: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/querying/basics/
SLS支持Prometheus中主要的幾個函數, 完整列表見: 時序數據查詢分析簡介_查詢與分析_時序存儲_日誌服務-阿里雲
單是看語法說明難免有些枯燥, 下面我們就進入實戰環節!
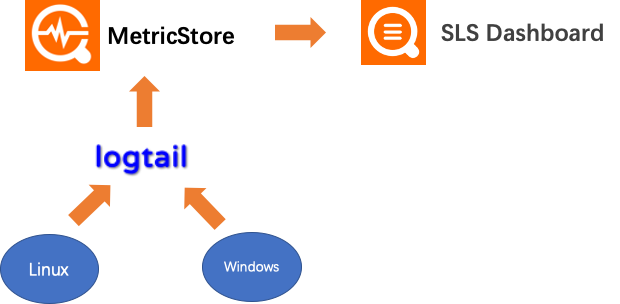
主機監控
主機監控我們採用logtail收集操作系統指標, 直接寫入Metric Store, 同時我們提供了內置的dashboard做可視化, 它的數據流如下:
操作步驟
新建logtail配置: 
選擇主機監控 
選擇機器組
確認插件配置 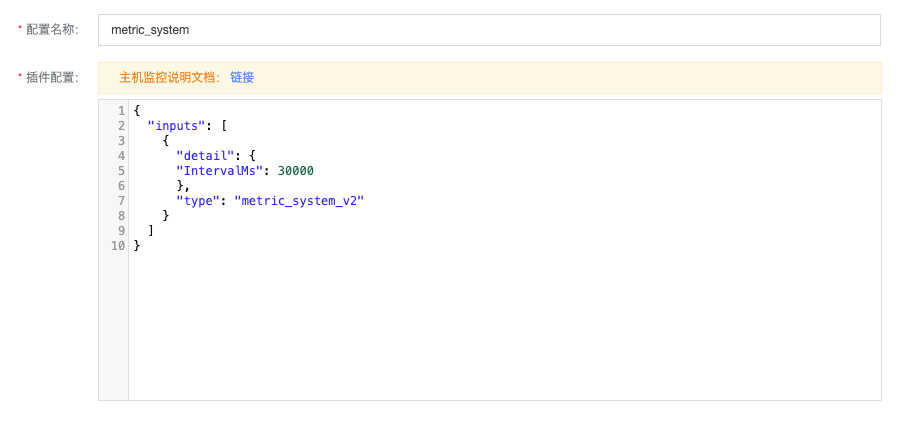
IntervalMs代表採集間隔, 默認30s, 可保持默認點擊下一步即可完成
創建完成後即可在左邊dashboard列表中找到主機監控 
稍等1-2分鐘即可看到數據產生
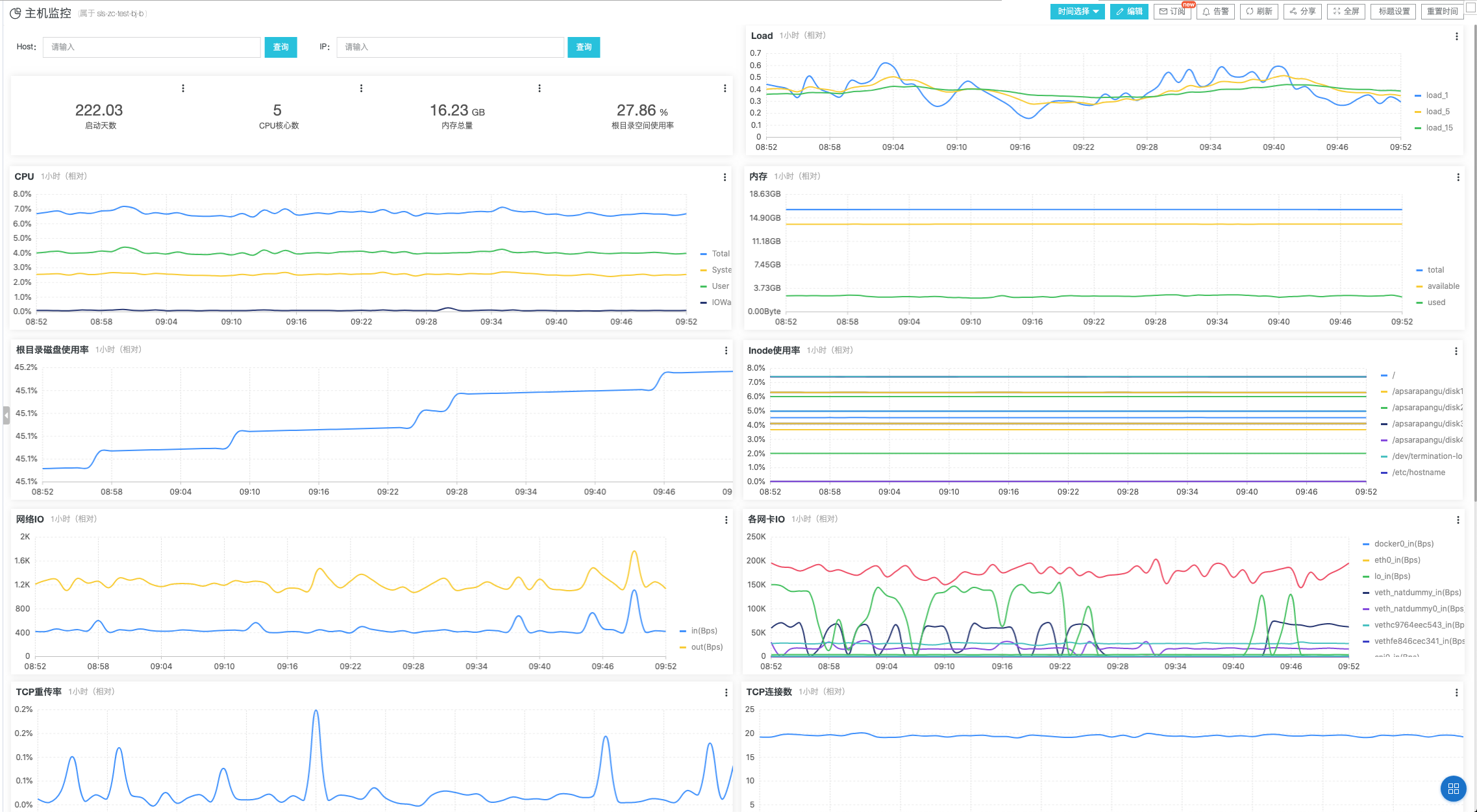
數據庫監控
數據庫監控採用telegraf進行採集, 並通過logtail支持的http receiver插件傳輸數據, logtail將把數據寫入metric store 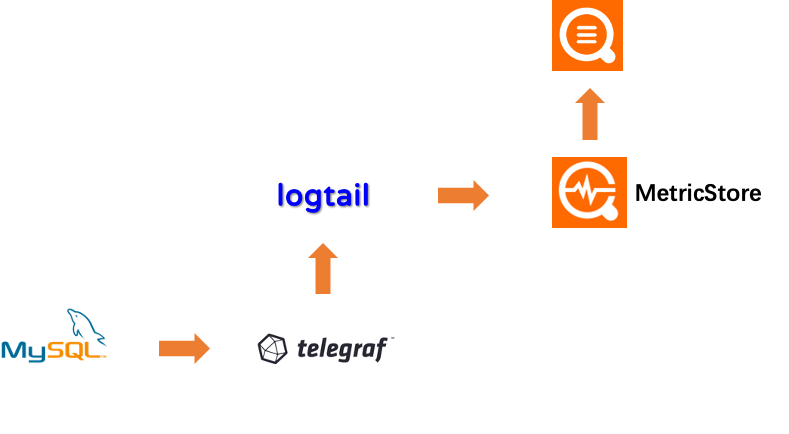
telegraf寫入logtail走influxdb協議, 因此在telegraf中按照influxdb配置即可
首先我們先創建一個logtail配置, 用於接收telegraf的數據, 新建logtail配置, 選擇自定義數據插件: 
選擇機器組(參照主機監控中的步驟) 輸入配置名稱, 並粘貼以下內容:
{
"inputs": [
{
"detail": {
"Format": "influx",
"Address": ":8476"
},
"type": "service_http_server"
}
],
"global": {
"AlwaysOnline": true,
"DelayStopSec": 500
}
}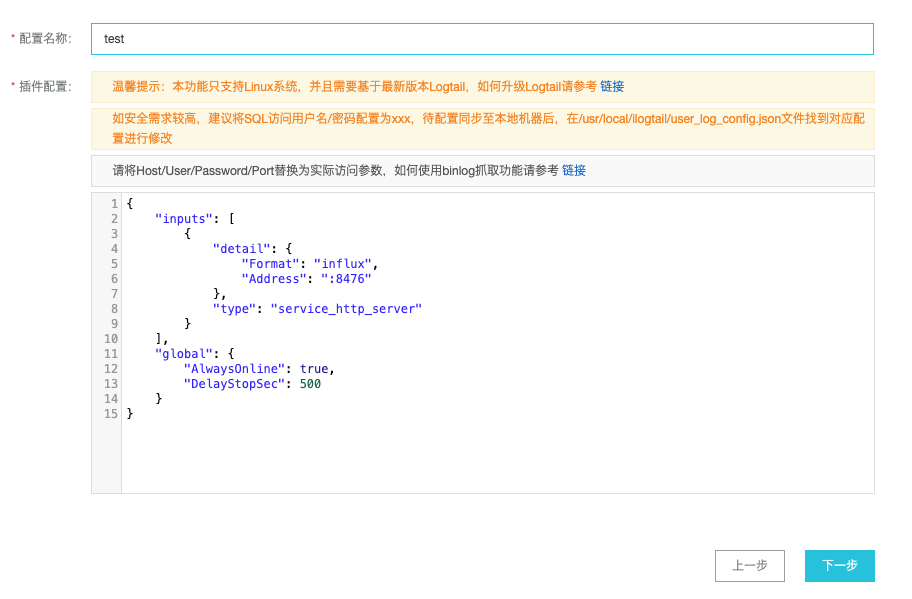
點擊下一步即可完成 接著我們開始配置telegraf 修改telegraf.conf, 默認在_etc_telegraf/telegraf.conf, 建議備份原文件, 新建並粘貼以下內容:
# Global tags can be specified here in key="value" format.
[global_tags]
# dc = "us-east-1" # will tag all metrics with dc=us-east-1
# rack = "1a"
## Environment variables can be used as tags, and throughout the config file
# user = "$USER"
# Configuration for telegraf agent
[agent]
## Default data collection interval for all inputs
interval = "10s"
## Rounds collection interval to 'interval'
## ie, if interval="10s" then always collect on :00, :10, :20, etc.
round_interval = true
## Telegraf will send metrics to outputs in batches of at most
## metric_batch_size metrics.
## This controls the size of writes that Telegraf sends to output plugins.
metric_batch_size = 1000
## Maximum number of unwritten metrics per output. Increasing this value
## allows for longer periods of output downtime without dropping metrics at the
## cost of higher maximum memory usage.
metric_buffer_limit = 10000
## Collection jitter is used to jitter the collection by a random amount.
## Each plugin will sleep for a random time within jitter before collecting.
## This can be used to avoid many plugins querying things like sysfs at the
## same time, which can have a measurable effect on the system.
collection_jitter = "0s"
## Default flushing interval for all outputs. Maximum flush_interval will be
## flush_interval + flush_jitter
flush_interval = "10s"
## Jitter the flush interval by a random amount. This is primarily to avoid
## large write spikes for users running a large number of telegraf instances.
## ie, a jitter of 5s and interval 10s means flushes will happen every 10-15s
flush_jitter = "0s"
## By default or when set to "0s", precision will be set to the same
## timestamp order as the collection interval, with the maximum being 1s.
## ie, when interval = "10s", precision will be "1s"
## when interval = "250ms", precision will be "1ms"
## Precision will NOT be used for service inputs. It is up to each individual
## service input to set the timestamp at the appropriate precision.
## Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s".
precision = ""
## Maximum number of rotated archives to keep, any older logs are deleted.
## If set to -1, no archives are removed.
# logfile_rotation_max_archives = 5
## Override default hostname, if empty use os.Hostname()
hostname = ""
## If set to true, do no set the "host" tag in the telegraf agent.
omit_hostname = false
###############################################################################
# OUTPUT PLUGINS #
###############################################################################
# Configuration for sending metrics to Logtail's InfluxDB receiver
[[outputs.influxdb]]
## The full HTTP Logtail listen address
urls = ["http://127.0.0.1:8476"]
## Always be true
skip_database_creation = true再在telegraf.d目錄中新建mysql.conf文件, 粘貼以下內容:
[[inputs.mysql]]
## specify servers via a url matching:
## [username[:password]@][protocol[(address)]]/[?tls=[true|false|skip-verify|custom]]
## see https://github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql#dsn-data-source-name
## e.g.
## servers = ["user:passwd@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/?tls=false"]
## servers = ["user@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/?tls=false"]
#
## If no servers are specified, then localhost is used as the host.
servers = ["user:passwd@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/?tls=false"]
metric_version = 2
## if the list is empty, then metrics are gathered from all databasee tables
table_schema_databases = []
## gather metrics from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES for databases provided above list
gather_table_schema = false
## gather thread state counts from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROCESSLIST
gather_process_list = false
## gather user statistics from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.USER_STATISTICS
gather_user_statistics = false
## gather auto_increment columns and max values from information schema
gather_info_schema_auto_inc = false
## gather metrics from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_METRICS
gather_innodb_metrics = true
## gather metrics from SHOW SLAVE STATUS command output
gather_slave_status = false
## gather metrics from SHOW BINARY LOGS command output
gather_binary_logs = false
## gather metrics from SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES command output
gather_global_variables = true
## gather metrics from PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA.TABLE_IO_WAITS_SUMMARY_BY_TABLE
gather_table_io_waits = false
## gather metrics from PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA.TABLE_LOCK_WAITS
gather_table_lock_waits = false
## gather metrics from PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA.TABLE_IO_WAITS_SUMMARY_BY_INDEX_USAGE
gather_index_io_waits = false
## gather metrics from PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA.EVENT_WAITS
gather_event_waits = false
## gather metrics from PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA.FILE_SUMMARY_BY_EVENT_NAME
gather_file_events_stats = false
## gather metrics from PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA.EVENTS_STATEMENTS_SUMMARY_BY_DIGEST
gather_perf_events_statements = false
## the limits for metrics form perf_events_statements
perf_events_statements_digest_text_limit = 120
perf_events_statements_limit = 250
perf_events_statements_time_limit = 86400
## Some queries we may want to run less often (such as SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES)
## example: interval_slow = "30m"
interval_slow = ""
## Optional TLS Config (will be used if tls=custom parameter specified in server uri)
# tls_ca = "/etc/telegraf/ca.pem"
# tls_cert = "/etc/telegraf/cert.pem"
# tls_key = "/etc/telegraf/key.pem"
## Use TLS but skip chain & host verification
# insecure_skip_verify = false omit_hostname = false
[[processors.strings]]
namepass = ["mysql", "mysql_innodb"]
[[processors.strings.replace]]
tag = "server"
old = "127.0.0.1:3306"
new = "mysql-dev"
[[processors.strings.replace]]
tag = "server"
old = "192.168.1.98:3306"
new = "mysql-prod"注意修改servers字段為對應的MySQL連接串 重啟telegraf即可:
sudo service telegraf reload
# 或者
sudo systemctl reload telegraf稍等1-2分鐘刷新頁面, 選擇Metrics, 即可看到數據, MySQL監控暫時未提供預置dashboard, 可自行配置, 後續SLS將對常用數據庫和中間件提供默認dashboard模板
應用監控
應用監控中我們以Spring Boot應用為例, 使用Spring Boot Actuator暴露數據, 通過Prometheus採集, 並使用remote write 協議寫入Metric Store, 再使用Grafana對接做可視化, 整個數據流如下: 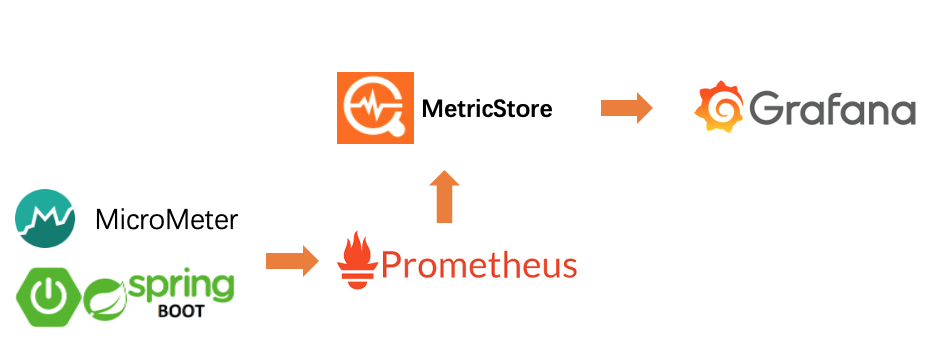
首先我們需要引入兩個依賴:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency>接著修改spring boot配置, 默認在resources/application.yml, 沒有的話請創建:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: spring-demo # 修改成您的應用名
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: 'prometheus' # 暴露/actuator/prometheus
metrics:
tags:
application: ${spring.application.name} # 暴露的數據中添加application label啟動應用, 訪問http://localhost:8080/actuator/prometheus, 應該看到如下數據:
# HELP jvm_memory_committed_bytes The amount of memory in bytes that is committed for the Java virtual machine to use
# TYPE jvm_memory_committed_bytes gauge
jvm_memory_committed_bytes{application="spring-demo",area="heap",id="PS Eden Space",} 1.77733632E8
jvm_memory_committed_bytes{application="spring-demo",area="nonheap",id="Metaspace",} 3.6880384E7
jvm_memory_committed_bytes{application="spring-demo",area="heap",id="PS Old Gen",} 1.53092096E8
jvm_memory_committed_bytes{application="spring-demo",area="heap",id="PS Survivor Space",} 1.4680064E7
jvm_memory_committed_bytes{application="spring-demo",area="nonheap",id="Compressed Class Space",} 5160960.0
jvm_memory_committed_bytes{application="spring-demo",area="nonheap",id="Code Cache",} 7798784.0
# HELP jvm_classes_unloaded_classes_total The total number of classes unloaded since the Java virtual machine has started execution
# TYPE jvm_classes_unloaded_classes_total counter
jvm_classes_unloaded_classes_total{application="spring-demo",} 0.0
# HELP jvm_memory_max_bytes The maximum amount of memory in bytes that can be used for memory management
jvm_memory_max_bytes{application="spring-demo",area="nonheap",id="Code Cache",} 2.5165824E8
# HELP jvm_classes_loaded_classes The number of classes that are currently loaded in the Java virtual machine
# TYPE jvm_classes_loaded_classes gauge
jvm_classes_loaded_classes{application="spring-demo",} 7010.0
# HELP jvm_threads_daemon_threads The current number of live daemon threads
# TYPE jvm_threads_daemon_threads gauge
jvm_threads_daemon_threads{application="spring-demo",} 24.0
# HELP jvm_threads_states_threads The current number of threads having NEW state
# 太長, 後面省略現在數據已經暴露出來了, 我們需要配置Prometheus進行採集, 修改Prometheus的配置文件:
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: "spring-demo"
metrics_path: "/actuator/prometheus"
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:8080"]
remote_write:
- url: "https://cn-zhangjiakou-share.log.aliyuncs.com/prometheus/sls-metric-store-test-cn-zhangjiakou/test-logstore-1/api/v1/write"
# - url: "https://sls-zc-test-bj-b.cn-beijing-share.log.aliyuncs.com/prometheus/sls-zc-test-bj-b/prometheus-spring/api/v1/write"
basic_auth:
username: ${accessKeyId}
password: ${accessKeySecret}
# Configures the queue used to write to remote storage.
queue_config:
max_samples_per_send: 2048
batch_send_deadline: 20s
min_backoff: 100ms
max_backoff: 5s
# max_retries: 10其中scrape_configs是用來採集我們的應用數據的, remote_write部分用於將數據寫入Metric Store, 注意替換basic_auth中的username和password為您對應的accessKeyId和accessKeySecret 配置完成後重啟Prometheus, 可訪問http://${prometheus_域名}/graph選擇metric查看是否採集成功 接著我們要配置grafana進行可視化 首先要把我們的Metric Store接入到Grafana的數據源中: 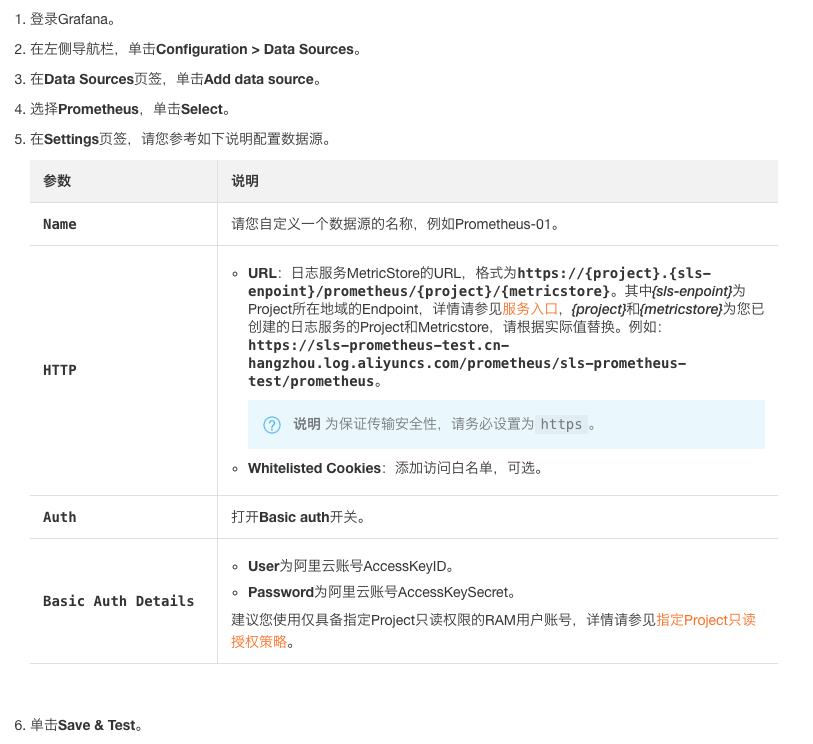
數據源接入成功後, 就可以配置dashbaord了, 我們已經在grafana.com上傳了模板: SLS JVM監控大盤(via MicroMeter) dashboard for Grafana | Grafana Labs 直接在grafana中導入即可: 做側邊欄選擇+ Import 粘貼url: https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/12856 選擇上一步創建的數據源 點擊Load 這樣就配置完成了, 我們完整的dashboard是這樣的:
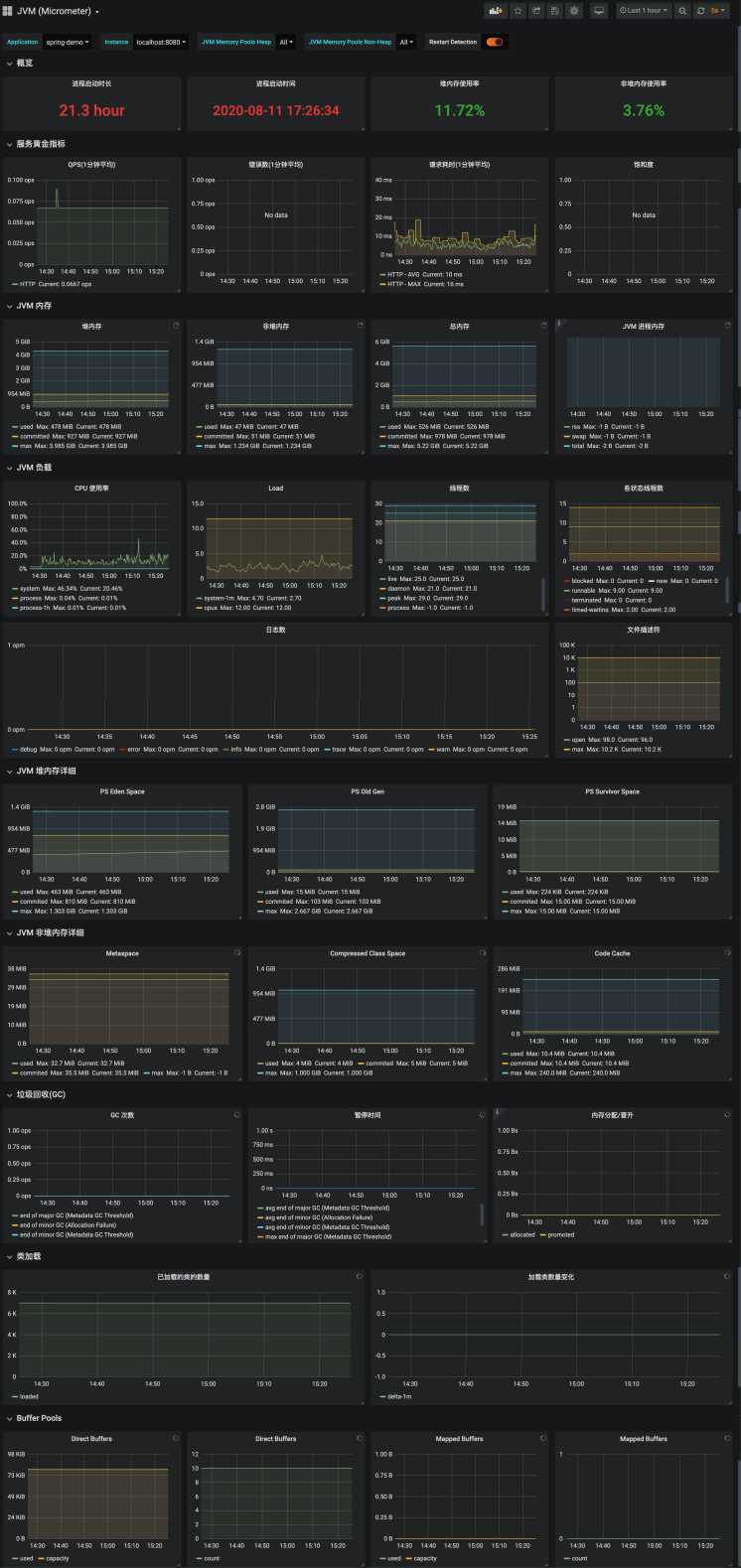
總結
我們首先介紹了SLS時序數據的查詢方式, 接著我們通過主機監控, MySQL監控, Spring Boot應用監控三種監控類型向大家分別展示了多種不同的數據接入, 可視化方法, 大家可以根據自身的環境選擇最容易使用的方式進行接入, 當數據都存儲在SLS上以後, 就可以使用SLS提供的SQL語法, PromQL語法對數據進行分析挖掘, 祝大家使用愉快! 如有任何問題, 可提工單, 或在用戶群中反饋(見下放釘釘二維碼), 也歡迎關注我們的微信公眾號, 會推送實用的使用技巧和最佳實踐哦~ 