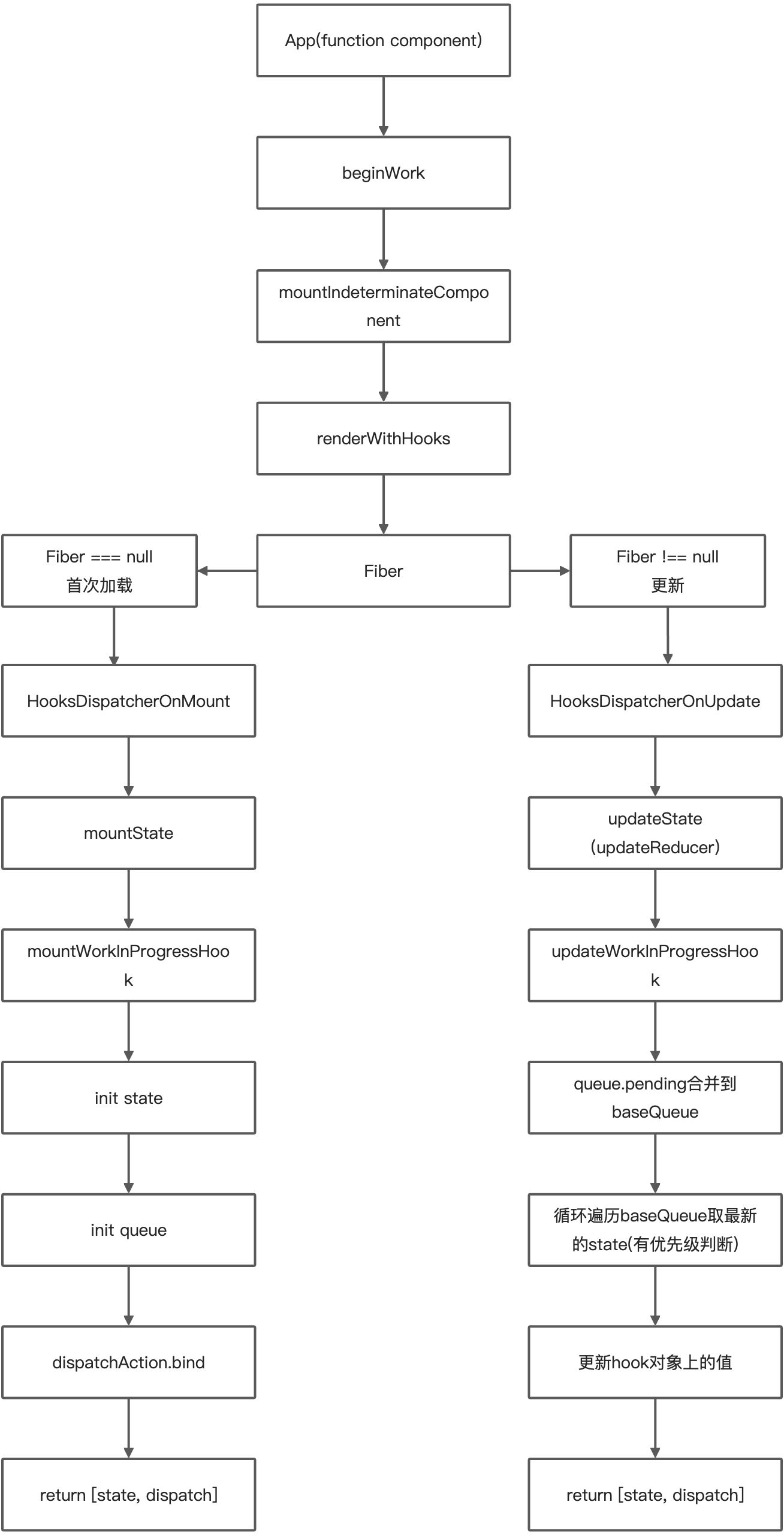
前言
自從react 官方發佈react hooks以來,項目開發組件時幾乎都是使用函數式組件來開發。在使用hooks過程中可以起到簡化代碼並邏輯清晰,對比於類組件能更易於理解代碼。網上也有很多關於這兩種組件的優劣勢對比,讀者可自行去翻閱。本主主要是想通過閱讀源碼來了解這背後的原理。(因為我不想成為API工程師,哈哈哈)
在這篇文章中,我想通過源碼的角度來分析下react hooks中的useState。假定讀者已經對react hooks有一定的使用並初步瞭解。(如果不瞭解建議去官網學習,react官網)
函數式組件和類組件
使用react開發基本上都是組件式開發,react組件分函數式組件和類組件。那函數式組件跟類組件的區別是什麼。下面看兩段代碼
函數式組件
import React from 'react';
const App = (props) => {
return <div>hello {props.user}<div>;
}
類組件
import React from 'react';
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: 'Damon',
};
}
componentDidMount() {}
render() {
return (
<>
<div>hello {this.props.user}</div>
<div>hello {this.state.name}</div>
</>
)
}
}
這兩段代碼除了沒有自身的狀態和生命週期外基本上算是等價的,那react發佈hooks想解決的問題就是讓函數式組件能擁有自身的狀態和生命週期。
在hooks還沒發佈時,函數式組件一直都是作為UI組件負責渲染視圖,沒有自身的狀態和 "生命週期函數" (當使用hooks開發時建議忘卻生命週期函數的概念),類組件有自身的狀態和生命週期函數可以處理複雜業務邏輯。
這兩種組件有個本質的區別:函數式組件會捕獲每次渲染時所用的值,類組件會創建一個實例來保存最新的值。
想深入瞭解的話可以閱讀此文函數式組件與類組件有何不同?作者是Dan Abramov(react核心開發人員之一)。
hooks 初始階段
分析源碼首先從引入hooks開始,以useState為例子。
import { useState } from 'react';
react/src/ReactHooks.js
可以來看下useState這個方法做了什麼 (簡化了代碼,去掉了類型和開發環境的提示)
export function useState(initialState){
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
}
調用useState等於是執行了 dispatcher.useState(initialState)
dispatcher是resolveDispatcher方法返回的,來看下這個方法做了什麼。
resolveDispatcher
function resolveDispatcher() {
const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
return dispatcher;
}
ReactCurrentDispatcher
react/src/ReactCurrentDispatcher.js
const ReactCurrentDispatcher = {
current: null,
};
export default ReactCurrentDispatcher;
其實看到這裡第一階段就已經結束了。ReactCurrentDispatcher.current初始化為null,先暫時記住這個接下來我們得從函數執行階段來看。
useState 初始化
看react渲染邏輯兜兜轉轉到 react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberBeginWork.js beginWork這個函數。benginWork函數通過傳入的當前的Fiber來創建子Fiber節點。會根據Fiber.tag來判斷生成不同的字節點。
function beginWork(
current, // 每次渲染的時候會產生一個current fiber樹,commit階段會替換成真實的dom
workInProgress, // 更新過程中,每個Fiber都會有一個跟其對應的Fiber,在更新結束後current會和workInProgress交換位置
renderLanes,
){
//... 先不關心其他邏輯
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
// 當function component第一次創建Fiber的時候,組件類型是 IndeterminateComponent (具體可以看createFiberFormTypeAndProps)
case IndeterminateComponent: {
return mountIndeterminateComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
workInProgress.type,
renderLanes,
);
}
}
}
function mountIndeterminateComponent(
_current,
workInProgress,
Component,
renderLanes,
) {
//...
value = renderWithHooks(
null, // 第一次渲染是null
workInProgress, // workInProgress fiber
Component, // 組件本身
props, // props
context, // 上下文
renderLanes,
);
}
export function renderWithHooks(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
props,
secondArg,
nextRenderLanes,
) {
renderLanes = nextRenderLanes;
currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress;
workInProgress.memoizedState = null;
workInProgress.updateQueue = null;
workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes;
// current === null 第一次渲染 current !== null 更新階段
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
current === null || current.memoizedState === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
// 函數組件被執行
let children = Component(props, secondArg);
// 這裡的邏輯先放一放
if (didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass) {}
// 當你不在函數組件內部執行hooks時候會拋出異常, ContextOnlyDispatcher對象方法都是拋出異常的方法
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
const didRenderTooFewHooks =
currentHook !== null && currentHook.next !== null;
renderLanes = NoLanes;
currentlyRenderingFiber = (null: any);
currentHook = null;
workInProgressHook = null;
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = false;
invariant(
!didRenderTooFewHooks,
'Rendered fewer hooks than expected. This may be caused by an accidental ' +
'early return statement.',
);
if (enableLazyContextPropagation) {
if (current !== null) {
if (!checkIfWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate()) {
const currentDependencies = current.dependencies;
if (
currentDependencies !== null &&
checkIfContextChanged(currentDependencies)
) {
markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate();
}
}
}
}
return children;
}
renderWithHooks 這個方法是函數執行的主要方法,首先是把memoizedState和updateQueue等於null,然後通過判斷current是否為null來賦值不同的hooks對象,current為null說明是第一次渲染不為null說明是更新,這裡第一次渲染跟更新是執行不同的hooks對象方法的。還記得第一階段看到ReactCurrentDispatcher.current嗎?就是在這裡被賦值的。
Component 調用是我們的函數組件被執行了,我們寫的邏輯就是在這裡被執行的。hooks也會依次按照順序執行。
hookDispatchOnMount 和 hookDispatchOnUpdate
hookDispatchOnMount是第一次渲染,hookDispatchOnUpdate是更新階段。
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
useCallback: mountCallback,
useContext: readContext,
useEffect: mountEffect,
useImperativeHandle: mountImperativeHandle,
useLayoutEffect: mountLayoutEffect,
useMemo: mountMemo,
useReducer: mountReducer,
useRef: mountRef,
useState: mountState,
useDebugValue: mountDebugValue,
useDeferredValue: mountDeferredValue,
useTransition: mountTransition,
useMutableSource: mountMutableSource,
useOpaqueIdentifier: mountOpaqueIdentifier,
unstable_isNewReconciler: enableNewReconciler,
};
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
useCallback: updateCallback,
useContext: readContext,
useEffect: updateEffect,
useImperativeHandle: updateImperativeHandle,
useLayoutEffect: updateLayoutEffect,
useMemo: updateMemo,
useReducer: updateReducer,
useRef: updateRef,
useState: updateState,
useDebugValue: updateDebugValue,
useDeferredValue: updateDeferredValue,
useTransition: updateTransition,
useMutableSource: updateMutableSource,
useOpaqueIdentifier: updateOpaqueIdentifier,
unstable_isNewReconciler: enableNewReconciler,
};
我們先來看看第一次渲染的mountState做了什麼。
function mountState(initialState){
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
initialState = initialState();
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue = (hook.queue = { // 更新隊列
pending: null, // 待更新
interleaved: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
dispatch: null, // 更新函數
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer, // 獲取最新的state
lastRenderedState: initialState, // 最後一次的state
});
// dispatchActio負責更新ui的函數
const dispatch = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
));
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
首先調用了mountWorkInProgressHook函數得到一個hook(待會來詳細看看這個方法幹了什麼),然後判斷initialState是否function,是的話執行得到state數據。接著把state賦值給了memoizedState和baseState。申明瞭一個queue對象,queue是個待更新隊列,dispatch是負責更新的函數,具體怎麼更新的在dispatchAction方法內可查看。
mountWorkInProgressHook
function mountWorkInProgressHook() {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null, // 不同的hook保存的不同 useState保存的是state useEffect保存的是 effect對象
baseState: null, // 最新的值
baseQueue: null, // 最新的隊列
queue: null, // 待更新隊列
next: null, // 指向下一個hook對象
};
// react hooks的數據結構是鏈表的方式,具體的邏輯就在這裡。
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// 函數內的第一個hooks就會走到這裡
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// 接下來每個hook都會被添加到鏈接到未尾
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
每次執行一個hooks函數都會調用這個方法來創建一個hook對象,這個對象裡保存了不同hook所對應的數據,最新的state數據,更新的隊列和指向下一個hook的對象。
來看個例子,看看為什麼不能在條件語句中申明hook
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
const App = () => {
const [name, setName] = useState('Damon');
const [age, setAge] = useState(23);
if (age !== 23) {
const Ref = useRef(null);
}
useEffect(() => {
console.log(name, age);
}, []);
return (
<div>
<span>{name}</span>
<span>{age}</span>
</div>
)
}
export default App;
當這個App組件被渲染的時候,workInProgressHook.memoizedState中會以鏈表的形式來保存這些hook。
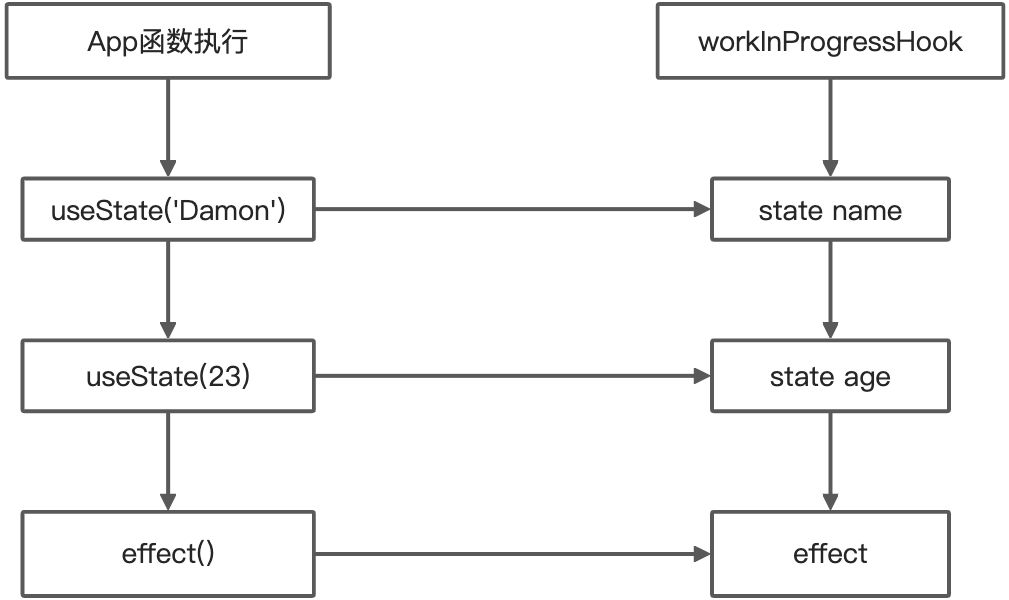
如果在條件語句中申明hook,那麼在更新階段鏈表結構會被破壞,Fiber樹上緩存的hooks信息就會和當前的workInProgressHook不一致,不一致的情況下讀取數據可能就會出現異常。
dispatchAction
dispatchAction這個是負責更新的函數,在mountState中通過bind綁定然後賦值給了dispatch。dispatch就是上面例子結構出來的setName。我們來看看這個函數又幹了什麼。
function dispatchAction(
fiber, // 當前的fiber數
queue, // mountState申明的更新隊列
action, // 這個就是我們setState傳進來的參數
) {
// 計算 expirationTime
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);
// react更新中都會有一個update
const update = {
lane,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: null,
};
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
// 判斷是否處於渲染階段
if (
fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber ||
(alternate !== null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber)
) {
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass = didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = true;
const pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
} else {
if (isInterleavedUpdate(fiber, lane)) {
const interleaved = queue.interleaved;
if (interleaved === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
update.next = update;
// At the end of the current render, this queue's interleaved updates will
// be transfered to the pending queue.
pushInterleavedQueue(queue);
} else {
update.next = interleaved.next;
interleaved.next = update;
}
queue.interleaved = update;
} else {
const pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
}
if (
fiber.lanes === NoLanes &&
(alternate === null || alternate.lanes === NoLanes)
) {
const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
let prevDispatcher;
try {
const currentState = queue.lastRenderedState; // 上一次state
// 這段邏輯會去進行淺對比,上一個state和當前state相等的話,就return界面不會更新
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
update.eagerReducer = lastRenderedReducer;
update.eagerState = eagerState;
if (is(eagerState, currentState)) {
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// Suppress the error. It will throw again in the render phase.
} finally {}
}
}
// 渲染更新
const root = scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
if (isTransitionLane(lane) && root !== null) {
let queueLanes = queue.lanes;
queueLanes = intersectLanes(queueLanes, root.pendingLanes);
const newQueueLanes = mergeLanes(queueLanes, lane);
queue.lanes = newQueueLanes;
markRootEntangled(root, newQueueLanes);
}
}
if (enableSchedulingProfiler) {
markStateUpdateScheduled(fiber, lane);
}
}
這段代碼還是比較複雜的,有一些和fiber相關的邏輯。但在這裡關於hooks的就是會創建一個update對象然後添加到queue鏈表上面,然後會判斷當前是否處於渲染階段,不是的話就會去獲取上一個state和當前的state進行淺對比,相等就會return不會執行更新,不相等就會執行scheduleUpdateOnFiber進行更新。
useState 更新
上面講了初始階段react會給ReactCurrentDispatcher.current賦值HooksDispatcherOnMount,更新階段賦值HooksDispatcherOnUpdate。在更新階段實際上調用的是updateState。
function updateState(initialState){
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, initialState);
}
function basicStateReducer(state, action){
// 這裡的action就是例子中的Damon。 const [name, SetName] = useState('Damon');
return typeof action === 'function' ? action(state) : action;
}
其實useState就是個簡化版的useReducer,看下useReducer幹了些啥。
updateReducer
function updateReducer(
reducer,
initialArg,
init,
){
//這裡是獲取當前的hooks,每一次函數更新的時候都會執行到hook,這個方法會保證每次更新狀態不丟失
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
//拿到更新隊列
const queue = hook.queue;
invariant(
queue !== null,
'Should have a queue. This is likely a bug in React. Please file an issue.',
);
// 調用lastRenderedReducer可獲取到state
queue.lastRenderedReducer = reducer;
// 拿到當前的函數內的hook
const current = currentHook;
let baseQueue = current.baseQueue;
const pendingQueue = queue.pending;
if (pendingQueue !== null) {
// 這裡主要是把baseQueue和pendingQueue做了交換,然後賦值到current上。
if (baseQueue !== null) {
const baseFirst = baseQueue.next;
const pendingFirst = pendingQueue.next;
baseQueue.next = pendingFirst;
pendingQueue.next = baseFirst;
}
current.baseQueue = baseQueue = pendingQueue;
queue.pending = null;
}
if (baseQueue !== null) {
const first = baseQueue.next;
let newState = current.baseState;
let newBaseState = null;
let newBaseQueueFirst = null;
let newBaseQueueLast = null;
let update = first;
// 這裡會循環的遍歷update
do {
const updateLane = update.lane;
// 這裡有涉及到優先級相關到邏輯
if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) {
const clone = {
lane: updateLane,
action: update.action,
eagerReducer: update.eagerReducer,
eagerState: update.eagerState,
next: null,
};
if (newBaseQueueLast === null) {
newBaseQueueFirst = newBaseQueueLast = clone;
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone;
}
currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes = mergeLanes(
currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes,
updateLane,
);
markSkippedUpdateLanes(updateLane);
} else {
// This update does have sufficient priority.
// 這個更新有足夠的優先級
if (newBaseQueueLast !== null) {
const clone = {
lane: NoLane,
action: update.action,
eagerReducer: update.eagerReducer,
eagerState: update.eagerState,
next: null,
};
newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone;
}
if (update.eagerReducer === reducer) {
newState = update.eagerState;
} else {
const action = update.action;
newState = reducer(newState, action);
}
}
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null && update !== first);
if (newBaseQueueLast === null) {
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
newBaseQueueLast.next = newBaseQueueFirst;
}
if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) {
markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate();
}
// 替換hook上的值
hook.memoizedState = newState;
hook.baseState = newBaseState;
hook.baseQueue = newBaseQueueLast;
queue.lastRenderedState = newState;
}
const lastInterleaved = queue.interleaved;
if (lastInterleaved !== null) {
let interleaved = lastInterleaved;
do {
const interleavedLane = interleaved.lane;
currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes = mergeLanes(
currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes,
interleavedLane,
);
markSkippedUpdateLanes(interleavedLane);
interleaved = interleaved.next;
} while (interleaved !== lastInterleaved);
} else if (baseQueue === null) {
queue.lanes = NoLanes;
}
const dispatch = queue.dispatch;
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
首先獲取了當前正在工作的hook,然後把queue.pending合併到baseQueue,這樣做其實是有可能新的更新還沒有處理,一次更新中可能會有多個setName,所以需要把queue.pending中的update合併到baseQueue內。接著會通過循環遍歷鏈表,執行每一次更新去得到最新的state,把hook對象的值更新到最新。然後返回最新的memoizedState和dispatch。這裡的dispatch其實就是dispatchAction,dispatchAction主要是負責更新界面的函數。
updateWorkInProgressHook
react中每一個hook更新階段都會調用updateWorkInProgressHook來獲取當前的hook。
function updateWorkInProgressHook() {
let nextCurrentHook;
if (currentHook === null) {
// 第一個hooks會走到這,然後在fiber memoizedState中獲取
// currentlyRenderingFiber.alternate 這個是當前的fiber樹
const current = currentlyRenderingFiber.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
nextCurrentHook = current.memoizedState;
} else {
nextCurrentHook = null;
}
} else {
// 因為是鏈表數據結構 其他的hook直接從next獲取
nextCurrentHook = currentHook.next;
}
let nextWorkInProgressHook;
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// 跟上面一樣 第一次執行hooks時候
nextWorkInProgressHook = currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState;
} else {
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
}
if (nextWorkInProgressHook !== null) {
workInProgressHook = nextWorkInProgressHook;
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
} else {
invariant(
nextCurrentHook !== null,
'Rendered more hooks than during the previous render.',
);
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
// 創建一個新的hook
const newHook: Hook = {
memoizedState: currentHook.memoizedState,
baseState: currentHook.baseState,
baseQueue: currentHook.baseQueue,
queue: currentHook.queue,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// 第一個hook添加到memoizedState和workInProgressHook
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = newHook;
} else {
// 其他的hook添加到鏈表末尾
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook;
}
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
這段代碼的作用主要是當函數每次更新的時候都會執行到hook,需要從fiber樹中找到對應的hook然後賦值到workInProgressHook上,這樣每次函數更新的時候狀態都不會丟失。
總結
最後來個分析的流程圖吧(本人水平有限,哈哈哈。歡迎一起交流學習)