
前言
對於iOS總體生態是比較封閉的,相比Android沒有像adb這種可以查看內存、cpu的命令.在日常做性能測試,需要藉助xcode中instruments查看內存、cpu等數據.
但是藉助instruments比較麻煩、又不能提供命令行.在持續集成中,很難時時的監控app的性能指標.並且現在app發版一般是2周左右,留給做專項測試的時間更少了,那麼做核心場景性能測試,肯定是來不及的.
所以需要藉助一些自動化工具來減輕手工採集性能指標的工作量.
性能採集項
app中基本性能採集項,內存、cpu、fps、電量等,因為自動化採集中手機設備是插著電腦充電的,所以不能採集電量數據.
已有工具
instruments是官方提供的,不能做到自動化採集
騰訊gt,需要在app中集成sdk,有一定的接入成本
第三sdk,類似騰訊gt需要在app集成,可能會有數據洩漏風險
腳本開發
上述的已有工具都不滿足,在持續集成中做到自動化採集性能數據,期望的性能測試工具有一下幾點:
方便接入
可生成性能報告
可持續化
數據收集精準
所以基於這幾點,需要自己開發一套性能採集腳本.
使用官方提供的api做性能採集
獲取內存、cpu等
import
/**
- 獲取內存
*/
-
(NSString *)get_memory {
int64_t memoryUsageInByte = 0;
task_vm_info_data_t vmInfo;
mach_msg_type_number_t count = TASK_VM_INFO_COUNT;
kern_return_t kernelReturn = task_info(mach_task_self(), TASK_VM_INFO, (task_info_t) &vmInfo, &count);
if(kernelReturn == KERN_SUCCESS) {memoryUsageInByte = (int64_t) vmInfo.phys_footprint; NSLog(@"Memory in use (in bytes): %lld", memoryUsageInByte);} else {
NSLog(@"Error with task_info(): %s", mach_error_string(kernelReturn));}
double mem = memoryUsageInByte / (1024.0 * 1024.0);
NSString *memtostring ;
memtostring = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%.1lf",mem];return memtostring;
}
/**
- 獲取cpu
*/
-
(NSString *) get_cpu{
kern_return_t kr;
task_info_data_t tinfo;
mach_msg_type_number_t task_info_count;task_info_count = TASK_INFO_MAX;
kr = task_info(mach_task_self(), TASK_BASIC_INFO, (task_info_t)tinfo, &task_info_count);
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) {return [ NSString stringWithFormat: @"%f" ,-1];}
task_basic_info_t basic_info;
thread_array_t thread_list;
mach_msg_type_number_t thread_count;thread_info_data_t thinfo;
mach_msg_type_number_t thread_info_count;thread_basic_info_t basic_info_th;
uint32_t stat_thread = 0; // Mach threadsbasic_info = (task_basic_info_t)tinfo;
// get threads in the task
kr = task_threads(mach_task_self(), &thread_list, &thread_count);
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) {return [ NSString stringWithFormat: @"%f" ,-1];}
if (thread_count > 0)stat_thread += thread_count;long tot_sec = 0;
long tot_usec = 0;
float tot_cpu = 0;
int j;for (j = 0; j < thread_count; j++)
{thread_info_count = THREAD_INFO_MAX; kr = thread_info(thread_list[j], THREAD_BASIC_INFO, (thread_info_t)thinfo, &thread_info_count); if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) { tot_cpu = -1; //return -1; } basic_info_th = (thread_basic_info_t)thinfo; if (!(basic_info_th->flags & TH_FLAGS_IDLE)) { tot_sec = tot_sec + basic_info_th->user_time.seconds + basic_info_th->system_time.seconds; tot_usec = tot_usec + basic_info_th->user_time.microseconds + basic_info_th->system_time.microseconds; tot_cpu = tot_cpu + basic_info_th->cpu_usage / (float)TH_USAGE_SCALE * 100.0; }} // for each thread
kr = vm_deallocate(mach_task_self(), (vm_offset_t)thread_list, thread_count * sizeof(thread_t));
assert(kr == KERN_SUCCESS);NSString *tostring = nil ;
tostring = [ NSString stringWithFormat: @"%.1f" ,tot_cpu];
NSLog (@"performance cpu:%@",tostring);return tostring;
}
獲取頁面vc
上邊收集了內存和cpu,還需要在收集數據的同時和頁面對應上.這樣就清楚了是當前頁面的內存和cpu情況.
/**
*獲取當前vc
*/
-
(UIViewController *) get_vc {
UIWindow *keyWindow = [UIApplication sharedApplication].keyWindow;
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{if ([keyWindow.rootViewController isKindOfClass:[UITabBarController class]]) { UITabBarController *tab = (UITabBarController *)keyWindow.rootViewController; UINavigationController *nav = tab.childViewControllers[tab.selectedIndex]; DDContainerController *content = [nav topViewController]; weakSelf.vc = [content contentViewController]; }});
return self.vc;
}
獲取設備信息
/*
*獲取設備名稱
*/
- (NSString *) get_devicesName {
NSString *devicesName = [UIDevice currentDevice].name; //設備名稱
NSLog(@"performance devicesName:%@", devicesName);
return devicesName;
}
/*
*獲取系統版本
*/
- (NSString *) get_systemVersion{
NSString *systemVersion = [UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion; //系統版本
NSLog(@"performance version:%@", systemVersion);
return systemVersion;
}
/*
*獲取設備idf
*/
- (NSString *) get_idf {
NSString *idf = [UIDevice currentDevice].identifierForVendor.UUIDString;
NSLog(@"performance idf:%@", idf);
return idf;
}
數據拼接
最終要把內存、cpu等數據拼接成字典的形式,方便輸出查看
輸出log日誌的數據格式
{
"cpu": "0.4",
"fps": "60 FPS",
"version": "11.2",
"appname": "xxxxxx",
"battery": "-100.0",
"appversion": "5.0.4",
"time": "2018-09-07 11:45:24",
"memory": "141.9",
"devicesName": "xxxxxx",
"vcClass": "DDAlreadPaidTabListVC",
"idf": "8863F83E-70CB-43D5-B6C7-EAB85F3A2AAD"}
開啟子線程採集
開一個子線程定時採集數據
/*
- 性能採集子線程
*/
-
(void) performancethread {
NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithBlock:^{NSLog(@"performance ======get performance======"); [self get_fps]; while (true) { DDPerformanceModel *model = [DDPerformanceModel new]; model.time=[self get_time]; model.appname=[self get_appname]; model.appversion=[self get_appversion]; model.idf =[self get_idf]; model.devicesName =[self get_devicesName]; model.version = [self get_systemVersion ]; model.vcClass = NSStringFromClass([self get_vc].class); model.memory = [self get_memory]; model.battery = [self get_battery]; model.cpu = [self get_cpu]; model.fps = self.percount; NSString *json = [model modelToJSONString];
// printf(" getperformance %srn", [json UTF8String]);
NSLog(@"getperformance model %@", json);
sleep(5);
}
}];
[thread start];
NSLog(@"performance ======continue mainblock======");}
初始化性能採集
AppDelegate.m文件中didFinishLaunchingWithOptions方法中用戶各種初始化操作,可以在第一行初始化性能採集,
這樣app啟動以後就可以定時採集數據
-
(BOOL)application:(UIApplication )application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary )launchOptions {
[[getperformance new] performancethread];//獲取性能數據 }性能採集日誌存儲
一般來說日誌存儲都是寫入到本地log日誌,然後讀取.但是有兩個問題
需要讀寫文件代碼,對於不熟悉oc的人來說比較難
因為是定時採集,文件IO操作頻繁
所以不考慮存儲本地log日誌的方式,可以在代碼中打印出數據,通過截獲當前設備運行的日誌獲取數據.
模擬器可以使用xcrun simctl命令獲取當前設備運行日誌,
真機用libimobiledevice獲取日誌
xcrun simctl spawn booted log stream --level=debug | grep getperformance
輸出log日誌的數據格式,這塊做了json美化,每歌幾秒在控制檯就打印一次
{
"cpu": "0.4",
"fps": "60 FPS",
"version": "11.2",
"appname": "xxxxxx",
"battery": "-100.0",
"appversion": "5.0.4",
"time": "2018-09-07 11:45:24",
"memory": "141.9",
"devicesName": "xxxxxx",
"vcClass": "DDAlreadPaidTabListVC",
"idf": "8863F83E-70CB-43D5-B6C7-EAB85F3A2AAD"}
如果獲取多次數據可以使用shell腳本把命令放到後臺,定時寫入到logpath中
nohup xcrun simctl spawn booted log stream --level=debug >${logpath} &
代碼插入到工程中
因為在持續集成中,每次打取的代碼都是不帶性能測試代碼,這些代碼是單獨寫到文件中.在編譯項目前,用shell把代碼插入到工程中,這樣打出來的包才能有採集性能數據功能.
scriptrootpath=${2}
AddFiles=${2}"/GetPerformance/performancefiles"
localDDPerformanceModelh=${scriptrootpath}"/GetPerformance/performancefiles/DDPerformanceModel.h"
localDDPerformanceModelm=${scriptrootpath}"/GetPerformance/performancefiles/DDPerformanceModel.m"
localgetperformanceh=${scriptrootpath}"/GetPerformance/performancefiles/getperformance.h"
localgetperformancem=${scriptrootpath}"/GetPerformance/performancefiles/getperformance.m"
addfiles(){
echo "刪除${projectaddpath}中的原性能採集文件"
rm -rf ${DDPerformanceModelh}
rm -rf ${DDPerformanceModelm}
rm -rf ${getperformanceh}
rm -rf ${getperformancem}
echo "複製文件到${projectaddpath}路徑"
cp ${localDDPerformanceModelh} ${projectaddpath}
cp ${localDDPerformanceModelm} ${projectaddpath}
cp ${localgetperformanceh} ${projectaddpath}
cp ${localgetperformancem} ${projectaddpath}
}
性能數據繪製
在手工和自動化使用插入性能測試代碼的app,如果截獲性能數據後,可以對數據做性能數據繪製.
用Higcharts或者echarts繪製性能走勢圖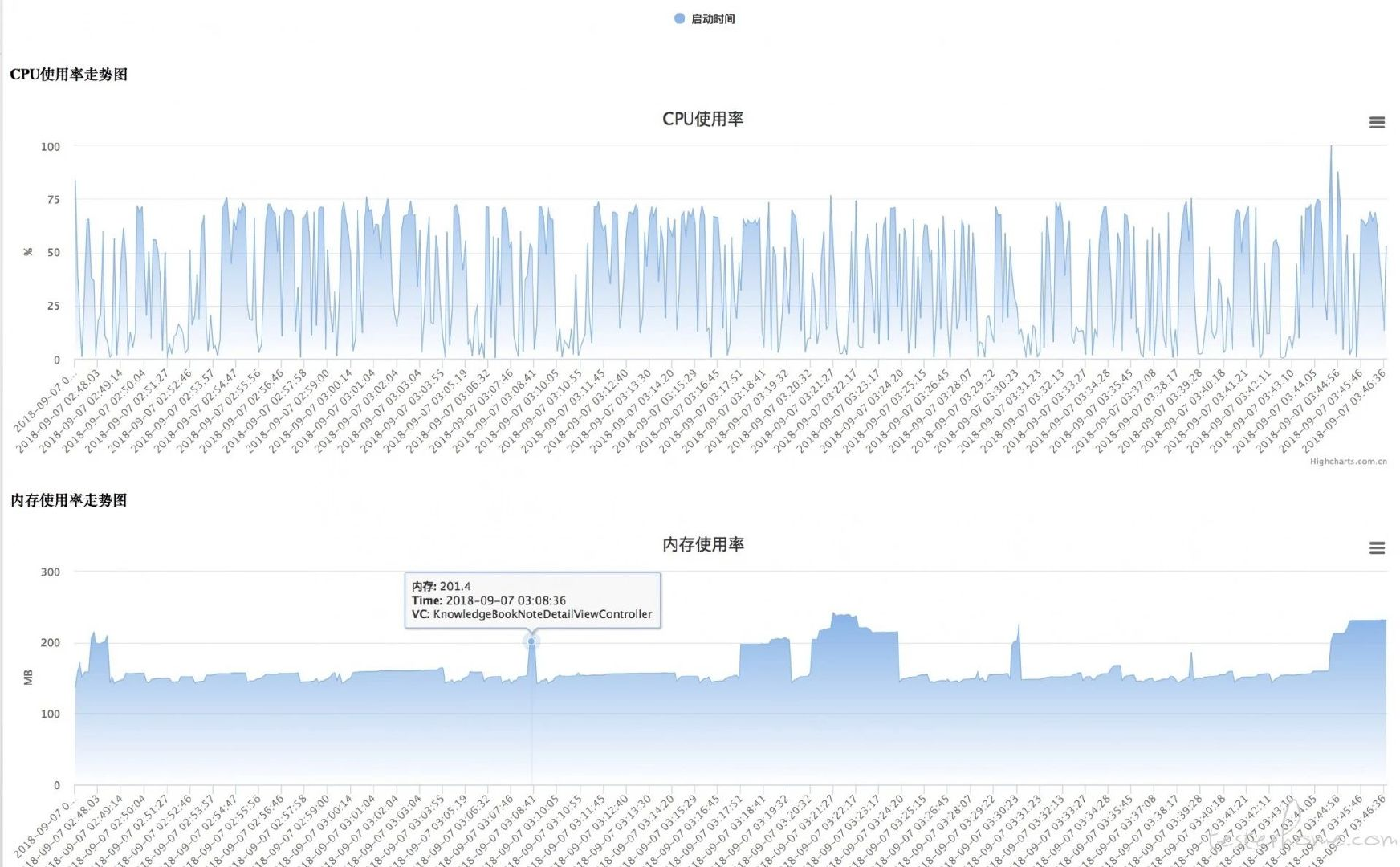
如何在持續集成中使用
monkey和UI自動化中使用,最終會發送一份性能報告.
Demo代碼
已經把性能代碼脫了主項目,可在Demo代碼中編譯,github地址:https://github.com/xinxi1990/iOSPerformanceTest
最後
雖然iOS生態封閉,但是對於開發者和測試者還是有一些空間可以利用的.
iOS測試一直都是一個難點,難懂的oc語法和iOS整體框架.如果你開始慢慢接觸iOS,會發現iOS測試也並不是那麼難,需要一點耐心和一點專心而已.
(文章來源於霍格沃茲測試學院)