上一篇:CGLIB實現代理設計模式 | 帶你學《Java語言高級特性》之九十六
【本節目標】
本節介紹了獲取Annotation信息的方法,以及Annotation的運行策略,通過案例解釋如何實現自定義的Annotation。
從JDK1.5後Java開發提供了Annotation技術支持,這種技術為項目的編寫帶來了新的模型,而後經過了十多年的發展,Annotation的技術得到了非常廣泛的應用,並且在所有的項目開發中都會存在。
獲取Annotation信息
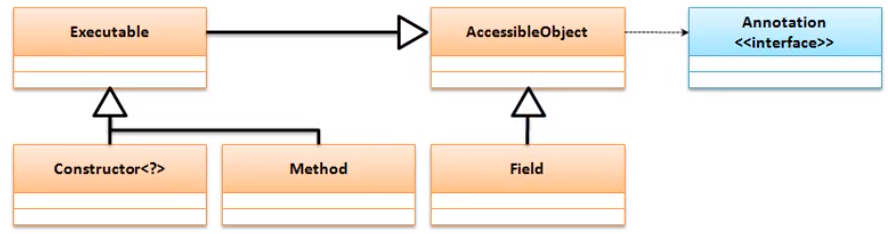
在進行類或方法定義時,都可以使用一系列的Annotation進行聲明,於是如果要想獲得這些Annotation信息,那麼可以直接通過反射來完成。在java.lang.reflect裡面有一個AccessibleObject類,在本類中提供有獲取Annotation類的方法:
獲取全部Annotation:public Annotation[] getAnnotations()
獲取指定Annotation:public <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass)
範例:定義一個接口,並在接口在使用Annotation
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class JavaAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
{ //獲取接口上的Annotation信息
Annotation annotations [] = IMessage.class.getAnnotations(); //獲取接口上的全部Annotation
for (Annotation temp : annotations) {
System.out.println(temp);
//@java.lang.FunctionalInterface()
//@java.lang.Deprecated(forRemoval=false, since="1.0")
}
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
{//獲取MessageImpl子類上的Annotation信息
Annotation annotations []= MessageImpl.class.getAnnotations(); //獲取類上的全部Annotation
for (Annotation temp : annotations) {
System.out.println(temp);
}
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
{ //獲取MessageImpl.toString()方法上的Annotation信息
Method method = MessageImpl.class.getDeclaredMethod("send", String.class);
Annotation annotations [] = method.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation temp : annotations) {
System.out.println(temp);
}
}
}
}
@FunctionalInterface //程序執行時可以獲取
@Deprecated(since = "1.0")
interface IMessage { //有2個Annotation
public void send(String msg);
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial") //無法在程序執行時獲取
class MessageImpl implements IMessage, Serializable {
@Override //無法在程序執行時獲取
public void send(String msg) {
System.out.println("【消息發送】" + msg);
}
}不同的Annotation有它的存在範圍,下面對比兩個Annotation:
@FunctionalInterface(運行時):
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface FunctionalInterface {}@SuppressWarnings(源代碼):
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE, MODULE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface SuppressWarnings {}現在發現“@FunctionalInterface”是在運行時生效的Annotation,所以程序執行時可以獲取Annotation;而“@SuppressWarnings”是在源代碼編寫時有效。
在RetentionPolicy枚舉類中還有一個class的定義,指的是在類定義時生效。
自定義Annotation
現在已經清楚了Annotation的獲取,以及Annotation的運行策略,但是最為關鍵性的因素是如何實現自定義的Annotation呢?為此在Java中提供了新的語法,使用“@interface”來定義Annotation。
範例:自定義Annotation
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //定義Annotation的運行策略
@interface DefaultAnnotation { //自定義的Annotation
public String title(); //獲取數據
public String url() default "www.mldn.cn"; //獲取數據
class Message {
@DefaultAnnotation(title = "MLDN")
public void send(String msg) {
System.out.println("【消息發送】" + msg);
}
}
public class JavaAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Method method = Message.class.getMethod("send",String.class); //獲取指定方法
DefaultAnnotation anno = method.getAnnotation(DefaultAnnotation.class); //獲取指定的Annotation
//System.out.println(anno.title()); //直接調用Annotation中的方法 MLDN
//System.out.println(anno.url()); //直接調用Annotation中的方法 www.mldn.cn
//直接調用Annotation中的方法
String msg = anno.title()+"("+anno.url()+")"; //消息內容
method.invoke(Message.class.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(), msg); //【消息發送】MLDN(www.mldn.cn)
}
}使用Annotation之後的最大特點是可以結合反射機制實現程序的處理。
想學習更多的Java的課程嗎?從小白到大神,從入門到精通,更多精彩不容錯過!免費為您提供更多的學習資源。
本內容視頻來源於阿里雲大學