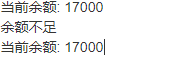本文來自於千鋒教育在阿里雲開發者社區學習中心上線課程《Python入門2020最新大課》,主講人姜偉。
案例講解
1、設計兩個類:
一個點類,屬性包括x,y座標。
一個Rectangle類(矩形),屬性有左上角和右下角的座標
方法:1.計算矩形的面積;2.判斷點是否在矩形內
實例化一個點對象,一個正方形對象,輸出矩形的面積、輸出點是在矩形內
class Point(object):
# Point 方法在創建時,需要兩個int類型的參數,用來表示x,y座標
def __init__(self, x: int, y: int):
self.x = x
self.y = y
class Rectangle(object):
def __init__(self, top_left: Point, bottom_right: Point):
self.top_left = top_left
self.bottom_right = bottom_right
def get_area(self):
# 面積:長 * 寬
length = abs(self.bottom_right.x - self.top_left.x)
width = abs(self.top_left.y - self.bottom_right.y)
return length * width
def is_inside(self, point):
# if self.bottom_right.x >= point.x >= self.top_left.x and self.top_left.y >= point.y >= self.bottom_right.y:
# return True
# else:
# return False
return self.bottom_right.x >= point.x >= self.top_left.x and self.top_left.y >= point.y >= self.bottom_right.y
p1 = Point(4, 20) # 定義左上角的點
p2 = Point(30, 8) # 定義右下角的點
r = Rectangle(p1, p2) # 把左上角和右下角的點傳遞給矩形
print(r.get_area()) # 312
# p = Point(10;, 13) # True
p = Point(20;, 30) # False
print(r.is_inside(p)) 2、寫一個計算器類,可以進行加、減、乘、除計算
class Calculator(object):
@staticmethod
def add(a, b):
return a + b
@staticmethod
def sub(a, b):
return a - b
@staticmethod
def mul(a, b):
return a * b
@staticmethod
def div(a, b):
return a / b
print(Calculator.add(4, 5)) # 9
print(Calculator.sub(4, 5)) # -1
print(Calculator.mul(4, 5)) # 20
print(Calculator.div(4, 5)) # 0.83、創建一個Person類,添加一個類字段用來統計Person類的對象的個數
class Person(object):
__count = 0 # 類屬性
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
x = object.__new__(cls) # 申請內存,創建一個對象,並設置類型是 Person 類
return x
def __init__(self, name, age):
Person.__count += 1
self.name = name
self.age = age
@classmethod
def get_count(cls):
return cls.__count
# 每次創建對象,都會調用 __new__ 和 __init__ 方法
# 調用 __new__ 方法,用來申請內存
# 如果不重寫 __new__ 方法,它會自動找object 的 __new__
# object 的 __new__ 方法,默認實現是申請了一段內存,創建一個對象
p1 = Person('張三', 18)
p2 = Person('李四', 19)
p3 = Person('jack', 20)
# print(Person.count) # 3
print(p1, p2, p3)
print(Person.get_count()) # 3
# p4 = object.__new__(Person) # 申請了內存,創建了一個對象,並設置它的類型是Person
# p4.__init__('tony', 23)
# print(p4)4、建立一個汽車類Auto,包括輪胎個數,汽車顏色,車身重量,速度等屬性,並通過不同的構造方法創建實例。至少要求汽車能夠加速、減速、停車。再定義一個小汽車類CarAuto繼承Auto並添加空調、導航屬性,並且重新實現方法覆蓋加速、減速的方法
class Auto(object):
def __init__(self, color, weight, speed=0, wheel_count=4):
self.wheel_count = wheel_count
self.color = color
self.weight = weight
self.speed = speed
def change_speed(self, x):
"""
修改車速
:param x: 表示要修改的車速值。如果是正數,表示加速,負數表示減速,0表示停車
"""
if x == 0:
self.speed = 0 # 如果傳遞的參數0,表示要停車
return
self.speed += x
if self.speed <= 0 and x < 0
return # return 後面可以什麼數據都不加,表示函數結束
class CarAuto(Auto):
def __init__(self, color, weight, ac, navigator, speed=0, wheel_count=4):
super(CarAuto, self).__init__(color, weight, speed, wheel_count)
self.navigator = navigator
self.ac = ac
car = CarAuto('白色', 1.6, '美的', 'Android', 10, 5)
car.change_speed(30)
print(car.speed) # 30
car.change_speed(-40)
print(car.speed) # 05.有一個銀行賬戶類Account,包括名字,餘額等屬性,方法有存錢、取錢、查詢餘額的操作。要求:
1.在存錢時,注意存款數據的格式
2.取錢時,要判斷餘額是否充足,餘額不夠的時候要提示餘額不足
class Account(object):
def __init__(self, name, balance):
self.name = name
self.balance = balance
def save_money(self, money):
assert isinstance(money, float) or isinstance(money, int), '請注意存錢數據的格式'
self.balance += money
def take_money(self, money):
if self.balance < money:
print('餘額不足')
else:
self.balance -= money
def check_balance(self):
return self.balance
a = Account('張三', 8000)
a.save_money(10000)
a.take_money(1000)
print('當前餘額:', a.check_balance())
a.take_money(20000)
print('當前餘額:', a.check_balance())